Following the CPU and GPU, the NPU (Neural Processing Unit) is the latest breakthrough, with companies leveraging its power to deliver advanced Generative AI features and experiences. Copilot+ PCs, equipped with Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X series processors, feature a robust NPU capable of up to 45 TOPS (trillion operations per second).
Apple’s newest Neural Engine, or NPU, achieves up to 38 TOPS. Meanwhile, Intel and AMD are set to release next-generation NPUs for their Lunar Lake (48 TOPS) and Strix Point (50 TOPS) platforms. With the growing buzz around NPUs, you might be wondering: what exactly is an NPU and what does it do? Here’s an explainer to address all your questions about NPUs.
What is an NPU?
NPU stands for Neural Processing Unit, and it is designed specifically for AI-related tasks. This includes processing neural networks, handling machine learning tasks, and managing various AI workloads.
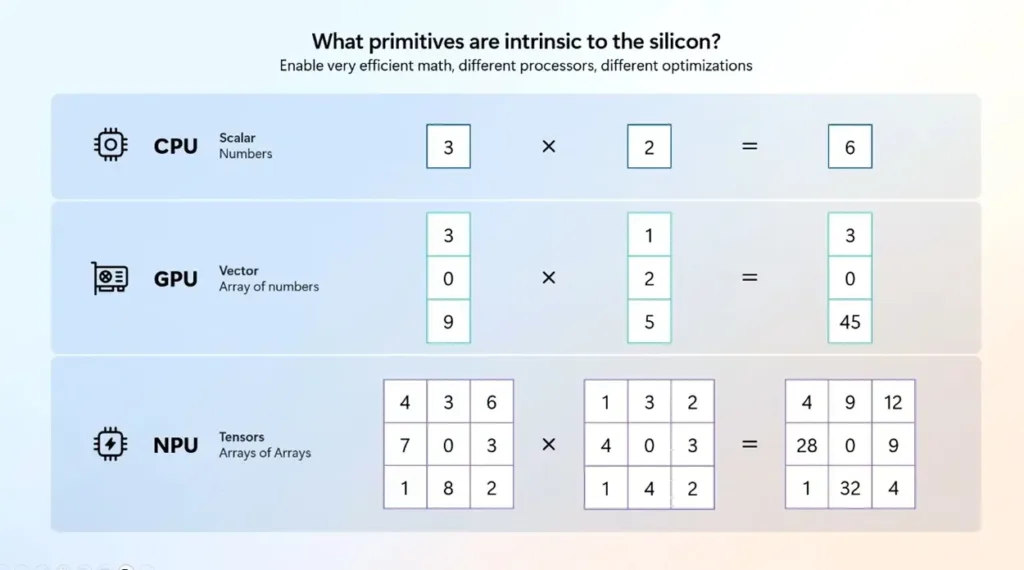
One of the key mathematical operations in AI is matrix multiplication (or ‘matmul’), which NPUs are optimized to perform at high speeds.
Moreover, parallel processing is crucial for AI tasks, as neural networks need to execute numerous operations simultaneously. NPUs are equipped with specialized accelerators that enable large-scale parallelism. With high-bandwidth memory, NPUs can efficiently perform parallel matrix multiplication operations across multiple cores.
In summary, NPUs are engineered for AI tasks with a focus on unlocking parallelism, executing matrix multiplication operations at high speeds, and providing scalability. Note that different companies use various names for similar technologies: Google refers to its NPU as the TPU (Tensor Processing Unit), while Apple calls it the Neural Engine.
How Does NPU Differ From CPU and GPU?
As mentioned earlier, NPUs are specialized for AI-related tasks, making them application-specific processing units. In contrast, CPUs are general-purpose processors built to manage a broad array of tasks.
For instance, CPUs manage operating system functions and general applications, showcasing their versatility by handling diverse workloads. They excel at single-threaded tasks but are less efficient with parallel processing tasks.
Next, GPUs are specifically designed for rendering graphics, making them ideal for powering games and creating simulations. GPUs are similar to NPUs in that they can handle tasks in parallel, which is why they are also used for AI-related tasks, particularly in training AI models. However, NPUs are optimized exclusively for AI operations, offering superior speed and efficiency in this domain.
Historically, before GPUs and NPUs, CPUs managed graphics through software rendering. The advancement of technology in the 1990s introduced GPUs with dedicated hardware for handling graphics. Today, we are experiencing the rise of NPUs, designed to further enhance AI processing capabilities.
These specialized compute units are designed to handle specific tasks, reducing the burden on the CPU and leading to improved efficiency and performance. While NPUs are gaining popularity for inferencing, GPUs continue to play a crucial role in training AI models. For instance, Google trained its Gemini model entirely using its TPU.
What are the Applications of NPU in Laptops?
Originally, NPUs and other specialized AI hardware accelerators were utilized primarily by large companies for parallel processing. Today, NPUs are also integrated into consumer products like laptops and smartphones. For instance, Microsoft’s new Copilot+ PCs feature a robust NPU that supports advanced functionalities such as Recall, which, although delayed, is expected to be available in the coming months.
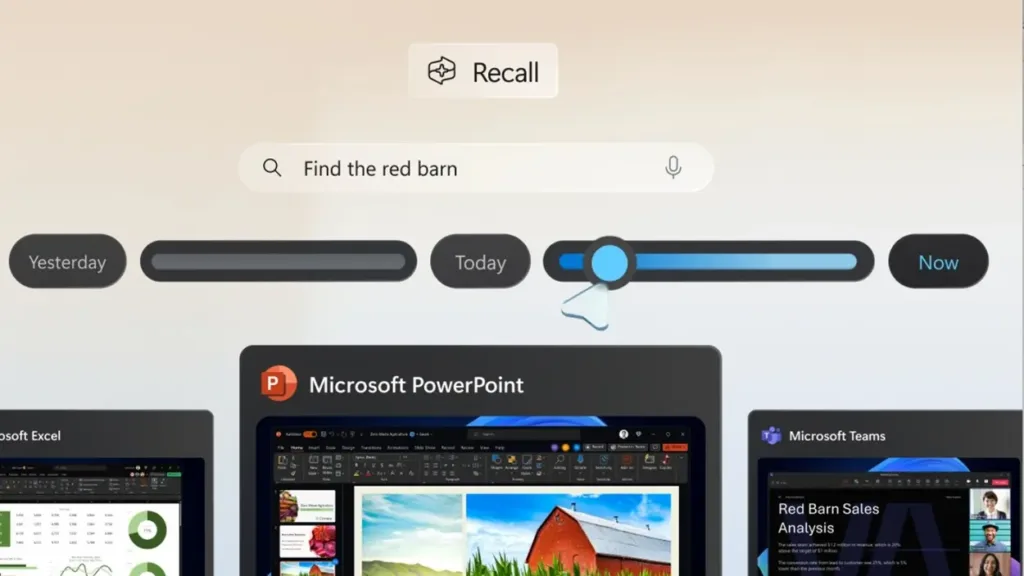
Recall captures screenshots, processes the data on the device using the NPU, and creates a vector index. If this processing were handled by the CPU or GPU, it would likely lead to significant battery drain. However, with a dedicated NPU, these AI operations are performed efficiently without impacting battery life or overloading the CPU or GPU.
Similarly, dedicated NPUs enable a range of features, such as Cocreator in MS Paint, image generation in the Photos app, background removal from video clips, visual effects with Magic Mask in DaVinci Resolve, frame upscaling in games, Windows Studio Effects, real-time translation and transcription, and more.
The use of NPUs is expected to expand significantly over time, relieving the CPU and GPU from handling certain tasks and thus improving device performance and battery efficiency.
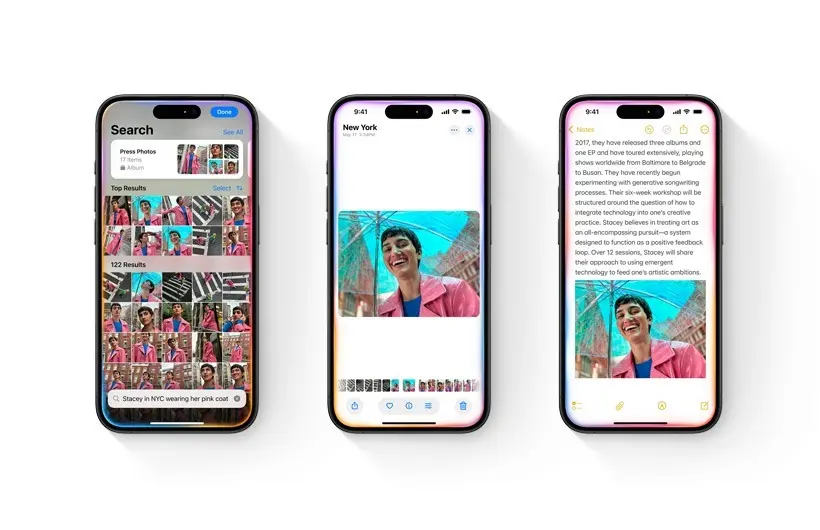
Apple, for instance, leverages its Neural Engine, also known as the NPU, to enhance various Apple Intelligence features across iOS, iPadOS, and macOS. This on-device AI model enables tasks such as summarizing emails, prioritizing notifications, generating summaries of call recordings, creating images, and more. The latest Siri also benefits from the Neural Engine for processing numerous AI tasks.
In essence, the NPU represents a new hardware accelerator poised to unlock exciting possibilities in the AI era. This is only the beginning, and we can expect new applications and experiences driven by NPUs in the near future.




