
As technology rapidly advances, AI increasingly infiltrates every aspect of our lives, simplifying tasks but raising concerns. This article delves into the growing threat of cyber attacks, leaving readers uneasy about the risks escalating by the second.
In the past year, global cyber attacks racked up a colossal $8 trillion in costs. The US alone suffered $9.48 million in losses this year, reported by IBM. With trends pointing to further increases, the outlook appears grim. Before delving into the unsettling broader perspective, let’s start with the fundamentals.
What constitutes a cyber attack?

The term “hacker” is familiar, with distinctions between ethical and malicious actors. When a hacker, motivated by malice, gains unauthorized access to a digital system, it constitutes a conventional cyber attack. Nowadays, these individuals or groups are often referred to as “threat actors” in cyberspace.
Daily, from inadvertently clicking on malicious links to experiencing hijacked Google and social media accounts, individuals expose themselves to cyber attacks. Over time, cyber attackers, cybercriminals, and threat actors have undergone various stages of evolution.
Nowadays, they possess diverse methods to identify and exploit vulnerabilities, all while concealing their activities behind a virtual barrier, making tracking them down a daunting task.
The most alarming aspect? Victims often remain unaware of cyber attacks until it’s too late. As American novelist Rebecca Brown aptly expressed, “You can’t combat a battle you’re unaware of. You can’t overcome an adversary you don’t even know is striking.”
What motivates individuals or groups to initiate a cyber attack?
Cybercriminals are primarily incentivized by financial gain, as evidenced by a Databasix report indicating that over 80% of data breaches are financially motivated. Moreover, the report highlights that cyber espionage accounts for 10% of these incidents. Yet, the motivations extend beyond these figures.
Hacktivist groups, motivated by intrinsic factors rooted in socio-political causes, are also significant threat actors. Additionally, some launch cyber attacks for competitive advantages or even terrorist motives. With these motivations in mind, let’s explore the various common types of cyber attacks orchestrated by these criminals.
Common Cyber Attack Types
Phishing Attack
In a phishing attack, cybercriminals impersonate organizations or companies to lure individuals. They send fraudulent emails containing malicious links, tricking recipients into clicking them under the guise of legitimacy. This compromises their data. For instance, last year, the YouTube account of Linus Tech Tips was compromised using a similar method.
Phishing attacks pose significant risks as they exploit human errors rather than technical flaws in digital systems. Recent studies indicate that phishing comprises 39.6% of all email attacks. Additionally, a Check Point report highlighted the growing threat of romantic phishing, a trend that has ensnared many individuals, particularly those using dating apps.
Malware Attack

Malware, in the form of software, infiltrates systems by injecting trojans, worms, or other viruses. These programs gradually compromise and bypass antivirus or security systems, rendering digital devices vulnerable to threat actors. Among malware attacks, “Trojans” are frequently utilized. Trojans masquerade as legitimate software while harboring malicious intent.
Even when downloading seemingly legitimate programs, there’s a risk of encountering Trojans. Once installed, these malicious programs inject loaders and execute malware into systems. This underscores the importance of refraining from installing Android APKs from unofficial sources. Recent statistics indicate that Trojans account for a concerning 58% of all malware.
Ransomware Attack
Continuing with malware, it’s crucial to address ransomware attacks, which afflicted 72.7% of organizations in 2023. What sets ransomware apart is its ability to encrypt victims’ files, rendering them inaccessible. Moreover, true to its name, these files remain encrypted or locked until a ransom is paid to the threat actors.
Thus, threat actors employing ransomware capitalize on the situation and demand substantial ransoms. Recent studies show that the average cost of a ransomware attack is around $4.54 million, with recovery expenses totaling approximately $1.85 million.
Moreover, the rise of cryptocurrency facilitates threat actors in evading detection, enabling them to escape with the ransom without leaving a trace. These attacks not only result in financial losses but also erode customer trust in the organization and inflict reputational harm on the affected company.
Data Extortion
Data extortion attacks share similarities with ransomware attacks. However, in contrast to ransomware, where access to data is blocked, data extortionists actively steal the data. They exploit vulnerabilities and infiltrate the victim’s system to accomplish this.
Upon gaining access, they meticulously search through the victim’s files, making copies of sensitive data. Subsequently, they leverage this information to blackmail the victim into paying a ransom for its return. This tactic featured in 27% of cyber attacks in 2023. Unfortunately, even if the ransom is paid, there’s no guarantee that the victims will retrieve their data.
DDoS Attacks
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks aim to disrupt websites or servers by overwhelming them with traffic from multiple sources. Threat actors orchestrate DDoS attacks by directing traffic through botnets, thereby overloading the targeted website or server. ChatGPT also experienced a DDoS attack recently, rendering the website inaccessible for several hours.
A Cloudflare report provides revealing statistics. It highlights an 85% surge in network-layer DDoS attacks in 2023 compared to 2022. Undoubtedly, DDoS has emerged as one of the prevalent cyber attack types in recent times.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks (MiTM)
In a Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) attack, the threat actor assumes the intermediary role in your communication channels. This enables them to intercept your online conversations and glean sensitive information, such as browser chats and emails
Moreover, they have the capability to manipulate conversations by posing as legitimate senders and transmitting messages to recipients. Wi-Fi eavesdropping stands out as a prevalent form of MiTM attack, representing nearly 35% of total incidents in 2023. The report also underscores the heightened risk of such cyber attacks on public Wi-Fi networks.
These are just a few examples of common cyber attack types. However, a new threat has surfaced: cyber attackers leveraging AI to their advantage.
Escalating Threat of AI-Based Cyber Attacks

In a recent collaboration, Microsoft and OpenAI collaborated to dismantle five state-sponsored hacking groups exploiting OpenAI’s LLMs (Large Language Models) such as ChatGPT for malicious purposes. OpenAI outlines these threat actors in a dedicated blog post, with Microsoft providing further insights in its own security blog.
While OpenAI’s research suggests that its AI technology provides “only limited, incremental capabilities for malicious cybersecurity tasks,” it’s important to acknowledge the role ChatGPT played in romance scams. Additionally, the issue of deepfakes presents a separate and concerning challenge.
In a recent incident that sent shockwaves through the internet, threat actors employed deepfake technology to defraud a multi-million dollar company of a staggering $26 million. Allegedly, the fraudster impersonated the Chief Financial Officer using a deepfake and conducted a video call with a finance employee based in Hong Kong, who promptly transferred the funds. However, the saga doesn’t stop there.
Today, threat actors are employing advanced AI and ML techniques for sophisticated attacks previously unseen. This aligns with reports of a threat actor known as GoldFactory utilizing “highly sophisticated” trojans in combination with deepfake technology to acquire facial IDs and gain access to banking applications.
Meanwhile, here in India, AI-driven deepfake audio scams have reached unprecedented levels. A survey indicates that AI voice cloning scams are particularly prevalent in India. Alarmingly, the same survey found that 70% of global respondents were unable to distinguish between an AI-generated voice and a genuine one. This highlights the severity of the issue. We recently created a reel addressing this concern. You can watch it below:
Moreover, deepfake technology was employed to manipulate the general election in Slovakia. During the elections, a party disseminated false information by circulating deepfake audios and videos featuring the Progressive Slovakia leader Michal Šimečka.
Furthermore, Google’s recent Cybersecurity Forecast 2024 report discussed how generative AI is complicating matters for defenders by providing additional tools for threat actors.
This underscores the alarming potential for malicious misuse of AI and the significant harm it can inflict on a large scale. With each passing day, these attacks continue to evolve, making the AI cybersecurity threat landscape increasingly tangible. Thanks (or not) to AI, the staggering costs of cyber attacks projected for 2024 and beyond are incredibly concerning to contemplate.
Projected Financial Impact of Cyber Attacks in 2024 and Beyond
As highlighted earlier, cyber attacks incurred an estimated $8 trillion worldwide in 2023 alone. Recent research indicates that this figure is projected to rise to $9.5 trillion in 2024. Furthermore, with the increasing use of AI technology in cyber attacks, experts anticipate this cost to surpass the $10 trillion mark by 2025. According to ExpressVPN, the global cost of cyber attacks may double in just five years. Here are the figures:
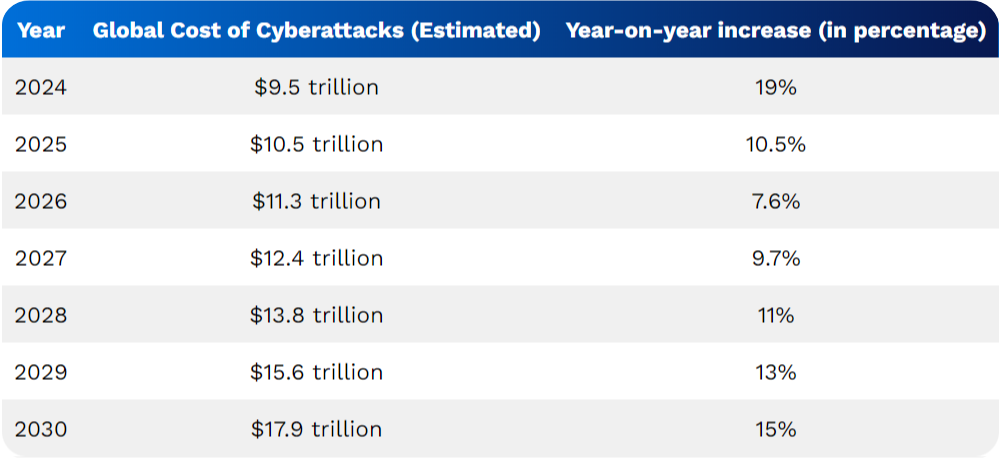
So, while these numbers provide a glimpse, only time will reveal the true extent of the financial impact. According to another Statista report, cybercrime costs are projected to soar to $23.84 trillion by 2027.
The reality is that cyber attackers are now operating on a scale of trillions and show no signs of slowing down. This is why, according to a report by Next Move Strategy Consulting, the cybersecurity market is forecasted to surpass the $650 billion milestone by 2030. As for the average cost of a data breach in 2023 by countries, here is the data.
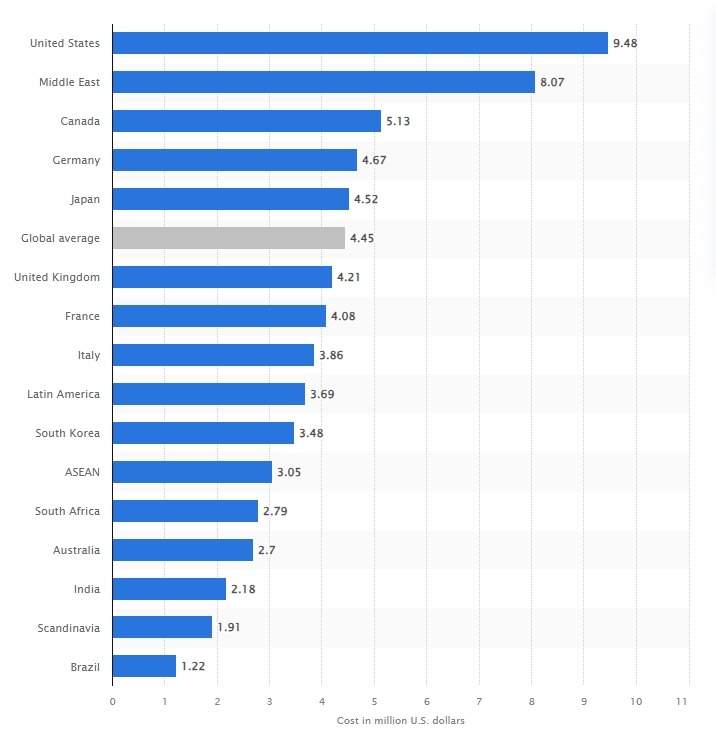
As depicted in this graph, the United States leads in recording the highest losses due to cybercrimes. In 2022, cyber attacks cost the US $9.44 million, increasing to $9.48 million in 2023, representing a 0.4% rise.
Similarly, the Middle East has experienced a surge in cyber attack costs, from $7.46 million in 2022 to $8.07 million in 2023, marking an alarming 8.1% increase.
Italy also witnessed an uptick, with costs rising from $3.74 million in 2022 to $3.86 million in 2023, a 3.2% increment. Latin America faced a substantial escalation, with costs soaring from $2.80 million in 2022 to $3.69 million in 2023, a staggering 31.7% rise.
ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) observed a 6.2% increase in cyber attack costs, from $2.87 million in 2022 to $3.05 million in 2023. ASEAN comprises countries like Vietnam, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, the Philippines, Cambodia, among others.
Meanwhile, countries such as Canada, Germany, Japan, the United Kingdom, France, South Africa, Australia, India, Scandinavia, and Brazil saw a decrease in cyber attack costs. However, the decline was marginal, and the costs still amounted to millions.
Most Common Targets of Cyber Attacks
Certain industries face heightened risks of cyber attacks due to the critical and sensitive data they manage. Among the most targeted sectors are those deemed “critical,” such as energy, healthcare, and finance. These industries attract attention from both profit-driven hacking groups and state-sponsored adversaries seeking to inflict harm on international rivals.
Additionally, other frequently targeted sectors include education, government, military, communications, managed service providers, and healthcare. Moreover, according to a report by IBM, certain industries have borne the brunt of the highest cyber attack costs. Please see the table below for details:

Based on this table, it’s evident that Healthcare, Finance, Pharmaceuticals, Energy, and Industrial sectors are the primary targets of cyber attacks, given their substantial costs incurred during the 2022-2023 period.
Notably, the Healthcare sector has repeatedly faced cyber attacks due to its handling of sensitive individual records, including medical history, personal information, and social security numbers. Such data can be exploited for insurance fraud, identity theft, and extortion.
The crucial question arises: With the staggering global cost of cyber attacks, how are these damages mitigated? Who ultimately bears the brunt of these losses?
How Are These Damages Dealt With?

According to IBM’s 2023 Cost of Data Breach report, the burden of cyber attacks falls on us, the users and customers. Let’s simplify this with an example: Imagine you’re subscribed to a particular software that you use regularly. If the company experiences a major cyber attack, it’s likely that your credentials and personal details are compromised.
After the company recovers, you may notice they’ve introduced a subscription plan for the software you rely on. Since you depend on it, you’re compelled to pay the new price. Essentially, the company leverages its customers to recoup the costs of these incidents and offset losses.
In this scenario, customers bear the brunt while the company mitigates its losses. However, can we fault companies for this approach? If they don’t recover costs, they risk going under. Ultimately, the blame lies with threat actors perpetrating these cyber attacks.
On a positive note, companies are increasingly turning to services like Cloudflare to safeguard their online platforms. They’re also implementing enhanced security protocols to fortify defenses against cyber threats. Additionally, educating employees on best practices, such as refraining from using personal computers for work, has become commonplace.
It’s crucial to recognize that if your personal device falls victim to an attack, threat actors can exploit it as a gateway to larger-scale breaches targeting your organization.
Tips for Protecting Yourself Against Cyber Attacks

Implement Multi-factor Authentication
In recent years, you may have come across the term “2FA“ frequently. Short for two-factor authentication, it provides an extra layer of security for your online accounts. Major platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Google strongly recommend enabling two-factor authentication for added protection.
By using 2FA, hackers face greater difficulty in bypassing your password and security measures. Additionally, it’s advisable to utilize trusted authenticator apps to enhance your online security further.
Use a VPN
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) offer a straightforward solution for safeguarding your online activities against threat actors. By masking your IP address with their server address, VPNs prevent it from being exposed online. This enables you to browse the web securely, free from concerns about hacking or compromise.
Moreover, VPNs employ encryption to ensure that your online data remains inaccessible to threat actors. Encrypted traffic poses a significant challenge for cyber attackers attempting to intercept and decipher it.
Be Cautious
Whether you’re navigating a dating app or checking your emails, exercise caution. Avoid engaging with suspicious accounts online or clicking on unfamiliar links without conducting proper research. Taking these precautions can help prevent potential mishaps and ensure that your actions don’t inadvertently expose you to risks. It’s always better to prevent than to seek a cure.
Report Suspicious Online Activities
In addition to exercising caution, don’t overlook any signs of malicious activities online. If you encounter any suspicious incidents, promptly report them to the relevant company or authority. According to IBM’s report, organizations take an average of 204 days to identify a data breach and an additional 73 days to contain it. Reporting such incidents promptly can expedite detection and neutralization processes.
Keep Software Updated
Your smartphone, laptop, and even your smartwatch receive software updates for a reason. These updates bring security patches to your digital devices, enhancing their resilience against cyber attacks. Through these updates, companies address exposed vulnerabilities.
If you’re using a device that has ceased to receive critical updates, we advise against using it for personal purposes. This underscores the importance of brands extending the support window for devices. Recently, both Google and Samsung announced seven years of software updates for their flagship devices. This extended support ensures ongoing security and functionality, highlighting its significance.
The Bottom Line

With cyber attacks inflicting trillions in damages and projections indicating their persistence, one cannot overlook potential solutions to curb this ongoing threat. A Harvard Business Review report from last year highlighted a staggering statistic: 80% of cyber attacks stem from “human error.” It’s clear that individuals like us are the primary vulnerability in this equation.
Despite increased cyber training and awareness efforts, the report underscores our susceptibility to falling victim to cyber attacks. However, it also presents a compelling notion: we can leverage AI to our advantage.
While threat actors utilize AI for nefarious purposes, defenders can employ it to thwart such attacks. According to the report, AI demonstrates an impressive 98% accuracy in detecting and classifying malicious emails. This sentiment is echoed in a blog post by Terranova Security, emphasizing AI’s ability to swiftly analyze multiple devices and identify vulnerabilities.
Indeed, AI outpaces humans in speed and efficiency when performing such tasks. By taking necessary precautions and enhancing cyber awareness, individuals can play a vital role in preventing cyber attacks. Organizations must also equip their employees with comprehensive cyber education to minimize human errors.
It’s evident that a significant reduction in human errors is crucial for effectively countering the wave of cyber attacks and curbing escalating costs year after year.




