
Nvidia has recently introduced RTX Video HDR, a feature that appears to be exclusive to RTX GPUs. The inclusion of Tensor Cores in Nvidia’s RTX graphics cards adds significant value, particularly for users with HDR monitors. The distinction between HDR (High Dynamic Range) and SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) is substantial, with HDR offering richer blacks, enhanced color reproduction, and increased brightness.
The Tensor Cores on RTX GPUs play a crucial role in powering features like DLSS 3.5 and the company’s AI-based frame-generation technology. Beyond advancements in ray tracing, these additional capabilities make the latest generation GPUs highly appealing. Nvidia had previously launched RTX Video Super Resolution (VSR), a technology designed to enhance the quality of video content through a deep learning framework.
Likewise, RTX Video HDR is a recent AI-driven technology from Nvidia that harnesses the previously untapped Tensor cores on your Nvidia RTX graphics card. In essence, Nvidia’s AI is trained to anticipate the appearance of HDR footage and replicate it when activating RTX Video HDR.
According to Nvidia’s FAQ, RTX Video HDR leverages AI and the tensor cores within RTX GPUs to “dynamically remap” SDR footage into HDR10. Upon activation, the feature works towards “enhancing the visibility, details, and vibrancy of streamed video content“, providing an improved viewing experience.

For those curious about the compatibility of Nvidia RTX Video HDR technology, any RTX GPU from the 20 series onwards supports this new feature. However, it’s important to note that this capability is not available for GPUs in the GTX series. The showcased example of RTX Video HDR in action is demonstrated with Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 3.
To fully appreciate the difference, it’s essential to have an HDR monitor and activate the feature. The provided image serves as a basic demonstration, and users are encouraged to use an actual HDR monitor for a more accurate assessment. Currently, NVIDIA RTX Video HDR is compatible with Chromium-based browsers, including Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome.
Enabling RTX Video HDR
To activate this feature, simply access the Nvidia Control Panel by right-clicking on your desktop. Navigate to the last menu on the left sidebar labeled ‘Video‘ and then choose ‘Adjust video settings.’
Subsequently, select the checkbox for High Dynamic Range under the RTX Video Enhancement features. Additionally, you have the option to enable RTX Video Super Resolution conveniently in this section.
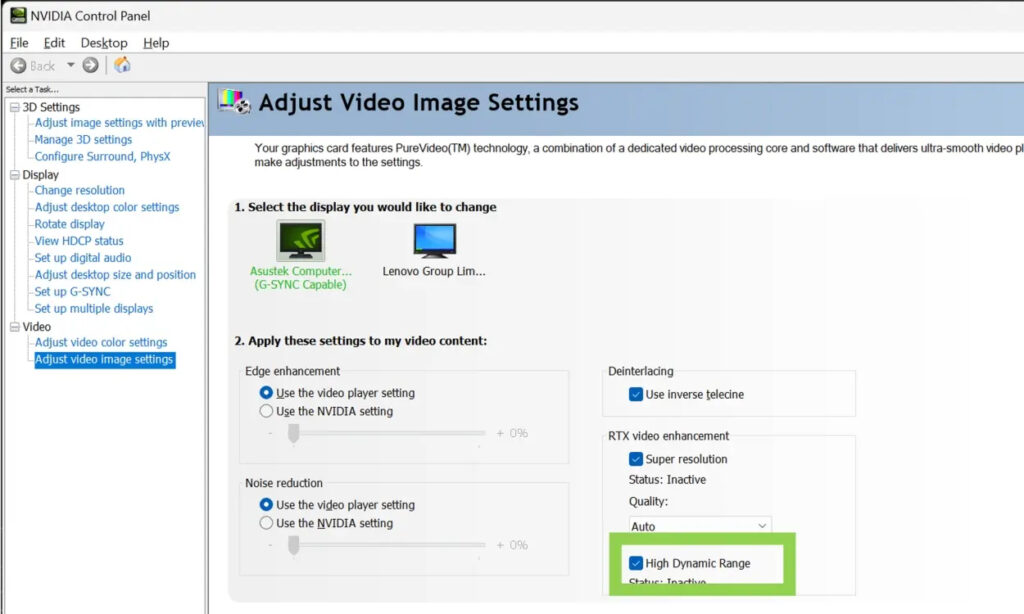
It’s important to note that Nvidia recommends having an HDR10-compatible monitor, and you must enable HDR in your Windows settings. By leveraging both RTX video enhancements (VSR and High Dynamic Range) on your RTX graphics card, you can upscale all media content, including browser videos and games.
When content is initially created in Standard Dynamic Range (SDR), the Tensor cores of your Nvidia RTX graphics card come into play, generating additional dynamic range. The outcome is an enhancement of standard quality videos to their optimal appearance. This form of AI technology proves to be remarkably more effective than many conventional tools currently available.

Both RTX Video Super Resolution and RTX Video HDR stand out as somewhat underrated features of Nvidia’s graphics cards, so it’s worth giving them a try. However, it’s essential to acknowledge that, despite the impressive results, this simulated HDR is powered by artificial intelligence.
What are your impressions of RTX Video HDR? Are you considering using features like this on your RTX GPU and making the most of those advanced Tensor cores? Share your thoughts in the comments below!




